Chemistry - Bonds - Covalent Bonds
Category: Chemistry
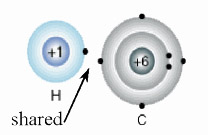
Image from UIC.EDU
Covalent bonds are the interatomic linkage that results from the sharing of an electron pair between two atoms. The binding arises from the electrostatic attraction of their nuclei for the same electrons. A covalent bond forms when the bonded atoms have a lower total energy than that of widely separated atoms.
Molecules that have covalent linkages include the inorganic substances hydrogen, nitrogen, chlorine, water, and ammonia (H2, N2, Cl2, H2O, NH3) together with all organic compounds. In structural representations of molecules, covalent bonds are indicated by solid lines connecting pairs of atoms.
A single line indicates a bond between two atoms (i.e., involving one electron pair), double lines (=) indicate a double bond between two atoms (i.e., involving two electron pairs), and triple lines (≡) represent a triple bond, as found, for example, in carbon monoxide (C≡O). Single bonds consist of one sigma (σ) bond, double bonds have one σ and one pi (π) bond, and triple bonds have one σ and two π bonds.
The idea that two electrons can be shared between two atoms and serve as the link between them was first introduced in 1916 by the American chemist G.N. Lewis, who described the formation of such bonds as resulting from the tendencies of certain atoms to combine with one another in order for both to have the electronic structure of a corresponding noble-gas atom.
Covalent bonds are directional, meaning that atoms so bonded prefer specific orientations relative to one another; this in turn gives molecules definite shapes, as in the angular (bent) structure of the H2O molecule. Covalent bonds between identical atoms (as in H2) are nonpolar�i.e., electrically uniform�while those between unlike atoms are polar�i.e., one atom is slightly negatively charged and the other is slightly positively charged. This partial ionic character of covalent bonds increases with the difference in the electronegativities of the two atoms.
Another explanation of covalent bonds is "A covalent bond is the chemical bond that involves the sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms when they share electrons is known as covalent bonding. For many molecules, the sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the equivalent of a full outer shell, corresponding to a stable electronic configuration."

 Back To Category Chemistry
Back To Category Chemistry